News center
Understanding Gelatin and Collagen: Key Components in Food Additives
Release time:
2025-04-13
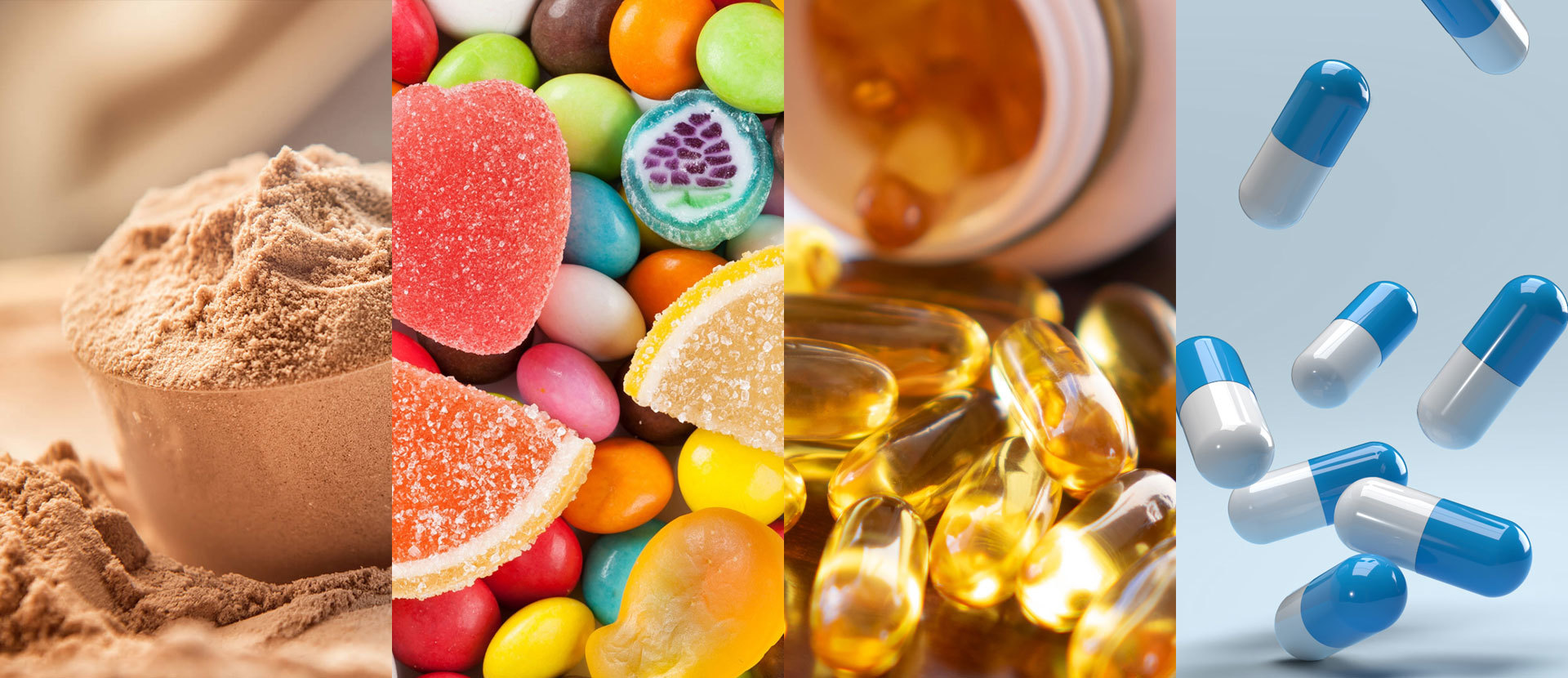
Gelatin and collagen are both vital components in the agricultural food sector, particularly as food additives. They play a crucial role in the texture, flavor, and stability of various food products. Gelatin is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient derived from collagen, which is a protein found in connective tissues of animals. Understanding the differences and similarities between these two substances is necessary for professionals in the food industry.
Collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals, comprising about 30% of the total protein content in the body. It serves as a critical structural component in skin, tendons, ligaments, and bones. When collagen is processed, usually through boiling or hydrolysis, it transforms into gelatin. This process not only breaks down collagen's complex structure but also makes it soluble in warm water, allowing it to be used in various culinary applications.
Gelatin is known for its gelling properties, which makes it a popular choice in the production of jellies, marshmallows, and desserts. Its ability to form a gel when cooled is utilized extensively in the food industry, providing a unique mouthfeel and enhancing the visual appeal of products. Additionally, gelatin acts as a thickener, stabilizer, and emulsifier, contributing to the overall quality of food items.
Both gelatin and collagen offer nutritional benefits as well. They are rich in amino acids, particularly glycine and proline, which are essential for maintaining skin elasticity, joint health, and muscle recovery. These health benefits have led to a growing interest in collagen supplements and food products that promote wellness, making it an attractive option for health-conscious consumers.
In the agricultural food industry, the sourcing of gelatin and collagen is a significant consideration. While traditional sources include animal by-products like bovine and porcine skins and bones, plant-based alternatives are gaining popularity due to the increasing demand for vegetarian and vegan options. Innovative techniques are being developed to extract similar gelling agents from algae and other plant sources, broadening the market potential for food manufacturers.
In conclusion, understanding gelatin and collagen is essential for professionals in the agricultural food industry. Their unique properties and nutritional benefits make them valuable food additives, enhancing product quality and consumer experience. As the market evolves, staying informed about advancements in sourcing and applications of these substances will be key to meeting consumer demands and industry standards.
Collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals, comprising about 30% of the total protein content in the body. It serves as a critical structural component in skin, tendons, ligaments, and bones. When collagen is processed, usually through boiling or hydrolysis, it transforms into gelatin. This process not only breaks down collagen's complex structure but also makes it soluble in warm water, allowing it to be used in various culinary applications.
Gelatin is known for its gelling properties, which makes it a popular choice in the production of jellies, marshmallows, and desserts. Its ability to form a gel when cooled is utilized extensively in the food industry, providing a unique mouthfeel and enhancing the visual appeal of products. Additionally, gelatin acts as a thickener, stabilizer, and emulsifier, contributing to the overall quality of food items.
Both gelatin and collagen offer nutritional benefits as well. They are rich in amino acids, particularly glycine and proline, which are essential for maintaining skin elasticity, joint health, and muscle recovery. These health benefits have led to a growing interest in collagen supplements and food products that promote wellness, making it an attractive option for health-conscious consumers.
In the agricultural food industry, the sourcing of gelatin and collagen is a significant consideration. While traditional sources include animal by-products like bovine and porcine skins and bones, plant-based alternatives are gaining popularity due to the increasing demand for vegetarian and vegan options. Innovative techniques are being developed to extract similar gelling agents from algae and other plant sources, broadening the market potential for food manufacturers.
In conclusion, understanding gelatin and collagen is essential for professionals in the agricultural food industry. Their unique properties and nutritional benefits make them valuable food additives, enhancing product quality and consumer experience. As the market evolves, staying informed about advancements in sourcing and applications of these substances will be key to meeting consumer demands and industry standards.
NEWS