News center
The Role of Gelatin Additives in Hard Capsules: Enhancing Pharmaceutical Formulations
Release time:
2024-09-05
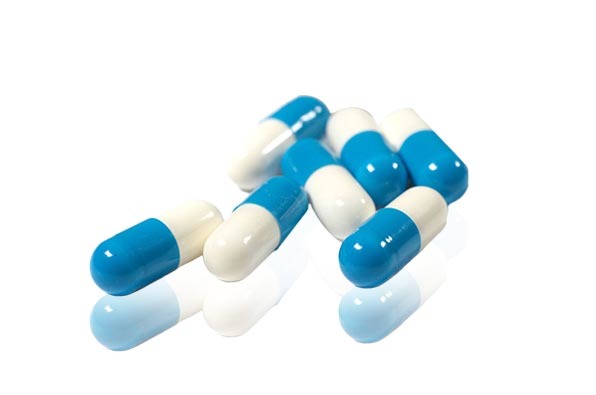
In the realm of pharmaceuticals, hard capsules are a popular dosage form due to their versatility, ease of swallowing, and efficient delivery of active ingredients. One of the key components in the formulation of these capsules is gelatin, a substance derived from collagen that plays a crucial role as an additive. Understanding the function and benefits of gelatin additives for hard capsules is essential for those involved in the medical and biopharmaceutical industries.
Gelatin serves multiple purposes in hard capsules. Firstly, it acts as a gelling agent, providing the necessary viscosity and structural integrity to the capsule shell. This is particularly important for ensuring that the capsules maintain their shape and stability throughout their shelf life. The ability of gelatin to form a gel-like consistency when hydrated allows for the creation of capsules that can effectively encapsulate powders, granules, or even liquids, making them a versatile option for various pharmaceutical applications.
Additionally, gelatin additives enhance the bioavailability of active ingredients. The gelatin shell dissolves in the gastrointestinal tract, allowing for the controlled release of the encapsulated substances. This targeted delivery is particularly beneficial for drugs that require specific absorption characteristics or for those that are sensitive to degradation in the acidic environment of the stomach.
Another significant advantage of gelatin is its biocompatibility. As a natural polymer, gelatin is generally well-tolerated by the human body, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions. This characteristic is particularly relevant in the biopharmaceutical sector, where the safety and efficacy of drug delivery systems are paramount. The use of gelatin additives aligns with the growing trend towards natural and biocompatible materials in drug formulations.
Moreover, gelatin possesses excellent film-forming properties, which contribute to the overall performance of hard capsules. The smooth surface of gelatin capsules improves the ease of swallowing, making them an appealing choice for patients, especially those who may have difficulty with other dosage forms. The aesthetic quality of gelatin capsules, including the ability to incorporate color and print, also supports branding and patient adherence to medication regimens.
It is important to note that while gelatin is widely used, there are alternatives available for individuals with dietary restrictions or allergies. For example, plant-based gelling agents such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) are increasingly being utilized to cater to vegetarian and vegan populations.
In summary, gelatin additives play a vital role in the formulation of hard capsules, enhancing their functionality, safety, and patient acceptability. As the pharmaceutical landscape continues to evolve, understanding these additives is crucial for developing effective and innovative drug delivery systems.
Gelatin serves multiple purposes in hard capsules. Firstly, it acts as a gelling agent, providing the necessary viscosity and structural integrity to the capsule shell. This is particularly important for ensuring that the capsules maintain their shape and stability throughout their shelf life. The ability of gelatin to form a gel-like consistency when hydrated allows for the creation of capsules that can effectively encapsulate powders, granules, or even liquids, making them a versatile option for various pharmaceutical applications.
Additionally, gelatin additives enhance the bioavailability of active ingredients. The gelatin shell dissolves in the gastrointestinal tract, allowing for the controlled release of the encapsulated substances. This targeted delivery is particularly beneficial for drugs that require specific absorption characteristics or for those that are sensitive to degradation in the acidic environment of the stomach.
Another significant advantage of gelatin is its biocompatibility. As a natural polymer, gelatin is generally well-tolerated by the human body, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions. This characteristic is particularly relevant in the biopharmaceutical sector, where the safety and efficacy of drug delivery systems are paramount. The use of gelatin additives aligns with the growing trend towards natural and biocompatible materials in drug formulations.
Moreover, gelatin possesses excellent film-forming properties, which contribute to the overall performance of hard capsules. The smooth surface of gelatin capsules improves the ease of swallowing, making them an appealing choice for patients, especially those who may have difficulty with other dosage forms. The aesthetic quality of gelatin capsules, including the ability to incorporate color and print, also supports branding and patient adherence to medication regimens.
It is important to note that while gelatin is widely used, there are alternatives available for individuals with dietary restrictions or allergies. For example, plant-based gelling agents such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) are increasingly being utilized to cater to vegetarian and vegan populations.
In summary, gelatin additives play a vital role in the formulation of hard capsules, enhancing their functionality, safety, and patient acceptability. As the pharmaceutical landscape continues to evolve, understanding these additives is crucial for developing effective and innovative drug delivery systems.
NEWS